
For many years now both quantum mechanics and wave theory have given equally valid alternative ways of looking at the world of atomic particles and empty space. But the mystery of the true nature of things grows deeper all the time. One entire school of thought in physics has been to treat empty space as truly empty. This posed no special problems for photons (light particles) because we can easily imagine particles hurtling from one place to another with nothing in between to impede them. The wave theory of light, on the other hand, left us with the problem in regard to the vacuum in that that we can not imagine waves without a medium which wiggles and moves in response to a stimulating source. However, by assigning arbitrary properties to the vacuum--namely an electric permeability and a magnetic permittivity--and by assuming the speed of light in free space was always constant, wave propagation in the vacuum of space was at least manageable.
It now appears that the vacuum has some remarkable properties. That is, it is not nothing! Empty space has elasticity and inertia--all media which transmit waves have these two properties. Switching to the Quantum Mechanics model it is now clear that photons traveling through empty space are constantly absorbed and re-emitted by "virtual particles" which continually appear and disappear everywhere in empty space! We have long known that when light photos enter glass or water or even air, it is the absorption and re-emission of the photons as they collide with matter that produces the speed of light which is characteristic of glass, water, or air. (These speeds are always less than the speed of light in vacuo).
A growing body of evidence now suggests that space itself can be stretched, bent, or distorted. In the vicinity of a massive object, such as the sun, the local "virtual particle density" of free space increases and light slows down and is bent when photons pass near the sun. There is no a priori reason for assuming the speed of light is a fixed constant, indeed the measured data and newer model of cosmology suggest it is not. Neither is the present value of c the highest possible velocity attainable--there is good reason to believe (1) that the speed of gravity is at least ten orders of magnitude greater than c.
The vacuum of "empty space" also appears to be an energy reservoir of immense capacity. Several elite scientific groups have been seeking practical ways of harnessing this "ZPE," ("zero-point energy"), for if it could be tapped it would be source of power that would make nuclear power seem old fashioned overnight. "Richard Feynman and others have pointed out that the amount of ZPE in one cubic centimetre of the vacuum is greater than the energy density in an atomic nucleus. In an atomic nucleus alone, the energy density is of the order of 1044 ergs per cubic centimeter. The minimum value that I have seen quoted for the ZPE is 1052 ergs per cubic centimeter…In actual practice, recent work suggests there may be an upper limit for the estimation of the ZPE at about 10114 ergs per cubic centimeter. In order to appreciate how large this quantity of energy is in each cubic centimeter of space, consider the most conservative estimate of 1052 ergs/cc. This is equivalent to the energy required to vertically lift 100,000 billion tonnes a distance of 1024 kilometers through a gravitational field as strong as at the earth’s surface. And 1024 km is roughly equivalent to 100 billion light years, about 5 times further than the most distant object observed in the universe! Another example may be in order. Most people are familiar with the light bulbs with which we illuminate our houses. The one in my office here is labeled as 150 watts. By comparison, our sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.8 x 1020 watts. In our galaxy there are in excess of 100 billion stars. Let us assume that they each radiate at roughly the same rate as our sun. Then the amount of energy expended by this whole galaxy of stars shining for one million years is roughly equivalent to the energy locked up in one cubic centimeter of space." (2)
In the first book of his science fiction trilogy, Out of the Silent Planet, (3) C.S. Lewis describes the abduction of Dr. Elwin Ransom, a Cambridge don, by an atheist physicist, Professor Edward Weston. The latter is bent on space conquest and other life forms because he views himself as superior to all. His god is the impersonal "Life Force." Along with his henchman Devine, Weston takes Ransom on a space trip to Mars, which, it turns out is indeed populated, as is Venus. Leaving the spiritual darkness of Earth, Ransom is elated by his awareness of space:
"But Ransom, as time wore on, became aware of an and more spiritual cause for his progressive lightening exultation of heart. A nightmare, long engendered in modern mind by the mythology that follows in the wake of science, was falling off him. He had read of 'Space': at the back of his thinking for years had lurked the dismal of the black, cold vacuity, the utter deadness, which supposed to separate the worlds. He had not known how it affected him till now--now that the very name seemed a blasphemous libel for this empyrean ocean radiance in which they swam. He could not call it 'dead'; he felt life pouring into him from it every moment. How should it be otherwise, since out of this ocean the all their life had come? He had thought it barren: that it was the womb of world, whose blazing an able offspring looked down nightly even upon the so many eyes--and here, with how many morel was the wrong name. Older thinkers had been wiser they named it the heavens." (3)
Lewis imagines great angels who have charge of whole planets and his depiction of evil is vivid and realistic. (4) Earth is the scene of the final conflict in Book Three because our dark planet is ruled by a mighty but "Bent" angel who seeks to maim and to destroy. Ransom, it turns out, is destined to play a part in God's program to save our race. The idea that space is filled with the presence of God, with life and power does not mean that the energy physicists attribute to the vacuum is identical with God nor would it be correct to attribute to the vacuum Weston's idea of the "Life Force." As I have suggested in an earlier article the aether, the vacuum of space, may be the interface between the material and the spiritual worlds. God supplies force and energy into our world from "the other side of the vacuum." The Apostle Paul said something like this when he spoke to the philosophers of Athens long centuries ago.
"The God who made the world and everything in it, being Lord of heaven and earth, does not live in shrines made by man, nor is he served by human hands, as though he needed anything, since he himself gives to all men life and breath and everything. And he made from one every nation of men to live on all the face of the earth, having determined allotted periods and the boundaries of their habitation, that they should seek God, in the hope that they might feel after him and find him. Yet he is not far from each one of us, for `In him we live and move and have our being'; as even some of your poets have said, `For we are indeed his offspring.'
The God of the Bible is separate (transcendent) from all that He has created. But He is also is a Personal and a Moral being. As the Apostle goes on to say, he holds all men accountable and will one day judge us all through His Son Jesus, raised from the dead:
Being then God's offspring, we ought not to think that the Deity is like gold, or silver, or stone, a representation by the art and imagination of man. The times of ignorance God overlooked, but now he commands all men everywhere to repent, because he has fixed a day on which he will judge the world in righteousness by a man whom he has appointed, and of this he has given assurance to all men by raising him from the dead."(Acts 17:24-31)
It is Jesus Christ who sits in the control room of the universe today directing the course of the stars and the plan of human events. It is He who is the appointed heir of all things and it is to this man that we all must give account!
Notes:
"As a professor of English at an evangelical school who does much work with Dante and C. S. Lewis, I'd like to add a few thoughts that are relevant to the resurgence of paganism.
In his Space Trilogy, Lewis offers an older, more medieval, more Dantean view of the cosmos that is radically different from our modem one. Space is not cold, dead, and meaningless; it is rich, vital, and filled with meaning and purpose. We live in what Dante would call a sympathetic universe: a universe in which the stars do have something to do with us, for both they and we were created by the same God, who is a God of harmony, order, and beauty. The stars do not control our destiny (as astrology presumes), but they are related to us and possess a reality that has bearing on our own.
Lewis was influenced by Dante (whose Divine Comedy presents a universe that shimmers with love, meaning, and vitality) and the writings of Owen Barfield (a fellow Inkling). Barfield argues in Saving the Appearances (and elsewhere) that in the past men did not perceive the natural world as a thing apart from themselves, to be studied and dissected coldly and rationally, but as a kindred spirit whose existence is interdependent on our own. Barfield calls this lost sympathy with nature "original participation" and calls for a return, albeit on a higher level, to a more human view of the cosmos that would grant the universe an eschatological purpose related to our own.
I truly feel that much of the reason that young people are abandoning the church for "New Age" is that they need to feel that they are a part of a living universe that is not just our house, but our home. To end with a paraphrase from Lewis's Voyage of the Dawn Treader, though a star may be made of burning gas, that is not what it is. Likewise I am made of flesh, blood, and sinew, but that is not who I am. I (and the star) am something more. Louis MARKOS, Houston (Texas) Baptist University.

From Barry Setterfield, 12/17/2022.
Thank you for the question on the speed of gravity, which, as Van Flandern pointed out must be close to instantaneous in our Solar System. The link that Lambert provided to the 1998 article I wrote is relevant. However, this work has been updated. I am committed until later this afternoon. So I will get a reply to you a bit later. In the meantime. attached is a segment from an article giving the basis of what is gravity. It can be extended to show that the force of gravity does not change with changes in the ZPE. Thus the orbit times of planets and stars remains unchanged over time. The reason is that all the variables in the equations cancel out leaving gravity acting in a consistent manner over time. In a word the quantity Gm in the equations which s doing the attracting is constant as the changes in G and m are mutually canceling.![]()
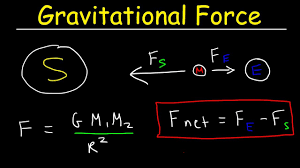
Update 12/22/22
by Barry Setterfield
Albert Einstein developed his theory of Relativity using two Postulates, both of which have proven to be incorrect. The Postulate of importance here is the invariance of the speed of light in a vacuum. Einstein developed his geometric theory of gravity after that Postulate was set in place. As a result, his theory of gravity requires that all gravitational interactions are propagated at the speed of light. This introduces a huge problem in our solar system to start with, and elsewhere in the universe as well. The problem is that, in our solar system, the action of gravity appears to be essentially instantaneous, rather than at the speed of light.
 The problem may be seen by the fact that it takes light just over 8 minutes to travel from the sun to the earth. If the gravitational pull from the sun takes 8 minutes to get to the earth, then the earth should be responding to where the sun was 8 minutes ago as seen from our location. If that was indeed true, then there would be a gravitational torque on the earth’s orbit causing the orbit to spiral into the sun. Obviously, this has not happened, and a number of scientists have analyzed the situation and come up with different theories of gravity to try and accommodate Einstein’s lightspeed requirement. One of these scientists was the late Dr. Thomas Van Flandern of the US Naval Observatory in Washington. His analysis revealed that for gravitational effects to be giving the results we observe in space, then the speed of gravity must be much higher than the current speed of light. The upper limit that Van Flandern determined was likely was obtained from the orbital characteristics of a star circling a “black-hole.” That velocity was about 2 x 10^10 the current speed of light. T. Van Flandern, J-P Vigier “Experimental Repeal of the Speed Limit for Gravitational, Electrodynamic, and Quantum Field Interactions,” Foundations of Physics, 32(7), pp.1-38, July 2002. Also T. Van Flandern, “Gravity,” in Pushing Gravity, M. R. Edwards, Ed., Apeiron, Montreal, 2002, pp. 93-122.
The problem may be seen by the fact that it takes light just over 8 minutes to travel from the sun to the earth. If the gravitational pull from the sun takes 8 minutes to get to the earth, then the earth should be responding to where the sun was 8 minutes ago as seen from our location. If that was indeed true, then there would be a gravitational torque on the earth’s orbit causing the orbit to spiral into the sun. Obviously, this has not happened, and a number of scientists have analyzed the situation and come up with different theories of gravity to try and accommodate Einstein’s lightspeed requirement. One of these scientists was the late Dr. Thomas Van Flandern of the US Naval Observatory in Washington. His analysis revealed that for gravitational effects to be giving the results we observe in space, then the speed of gravity must be much higher than the current speed of light. The upper limit that Van Flandern determined was likely was obtained from the orbital characteristics of a star circling a “black-hole.” That velocity was about 2 x 10^10 the current speed of light. T. Van Flandern, J-P Vigier “Experimental Repeal of the Speed Limit for Gravitational, Electrodynamic, and Quantum Field Interactions,” Foundations of Physics, 32(7), pp.1-38, July 2002. Also T. Van Flandern, “Gravity,” in Pushing Gravity, M. R. Edwards, Ed., Apeiron, Montreal, 2002, pp. 93-122.
Since the two postulates on which Einstein based his theory have been proven false it might be thought that all his predictions would be proven incorrect. This has not turned out to be the case because the effects of the ZPE have been shown to have the same results as Einstein's relativity did, but coming at it from an entirely different perspective. One of the papers involved in that discussion was my peer-reviewed article published in 2012 in the National Philosophy Alliance Conference Proceedings and can be found here: https://www.barrysetterfield.org/ZPE_and_relativity/ZPE_and_Relativity.html
The restrictive postulate which concerns us here is the speed of light. Einstein claimed that nothing could travel faster than lightspeed. However, determining exactly what that speed is needs some digging. Einstein assumed it was the current speed of light in a vacuum. However, the understanding of lightspeed has changed since Einstein's publications. The understanding of the action of the ZPE opens a new scenario. We now understand that the ZPE waves of energy crest and peak like waves on the ocean; and just as ocean waves form whitecaps and foam, which soon disappear, so, too do the ZPE waves form virtual particle pairs which appear and disappear.
The important point for our discussion is that light photons in transit interact with these virtual particle pairs, and this interaction slows them down. In 2013, Marcel Urban, the Research Director for the University of Paris demonstrated in a key article (in the European Physical Journal D on January 16th 2013) that the interactions of photons with the virtual particle pairs of the vacuum was the determining factor in lightspeed. In other words, knowing the number of virtual particle pairs and the interaction time, the present speed of light could be established. He showed that all photons of all wavelengths are uniformly affected. The conclusion is that when there are fewer Virtual Particle Pairs (VPP), lightspeed was higher and when there were more VPP's, then lightspeed was lower because of the interaction times of photons with VPP’s..
The number of VPP’s depend on the strength of the ZPE. In turn, the strength of the ZPE built up as the universe expanded, so VPP's also built up and lightspeed slowed down. In other words, without the VPP's, the speed of light would be very much higher as there would be fewer photon interactions. The picture that emerges is that, between interactions with the VPP’s, photons always travel at the same extremely high speed as they had originally. If we now propose that the speed of gravity is not subjected to the problems that light photons have with VPP's, but is unaffected by them, then as the number of VPP's built up and light photons were delayed in their travel, the gravitational interaction speed was not. This would indicate that, since the ZPE has built up by a factor of 3.13 x 10^9 lightspeed was initially higher by a similar factor at the inception of the cosmos. This would indicate that the speed of gravity then, being the same as the speed of gravity now, was also about 3.13 x 10^9 higher at least. This figure depends on the square-root of the Compton frequency of jiggle of subatomic particles; that is the square-root of (1.23 x 10^20) which is 1.1 x 10^10. For lightspeed, the VPP's require a factor to be introduced for their configuration. But, for gravitational interaction speed, that may not be necessary. As a result, the initial and continuing speed of gravity would be of the order of 1.1 x 10^10 faster than lightspeed today. This is in accord with Van Flandern's calculations from stellar orbits around black-holes etc.
The conclusion may well be that, whatever it is that transmits the force of gravity through space, it does not interact with the VPP’s of the vacuum. This leads to two possible scenarios.
In Scenario 1, while photons are simply bundles of electromagnetic energy, it might be considered that gravitational interactions are transmitted by bundles of gravitational energy. These gravitational bundles might not interact with the vacuum VPP’s because of their extremely small size. For this reason some consider these ”gravitons” to approximate to the Planck Length in size. This is the minimum size the fabric of space allows without the object being absorbed into the ‘gaps’ in the weave of the fabric. While gravitons are scientifically fashionable, their whole basis is speculative and unproven. Some theories require them and to some scientific minds that confirms they must exist.
Scenario 2 has a different approach which comes from the VPP’s themselves. The VPP’s are the reason why the speed of light changes with changing ZPE strength. However, between VPP interactions, the light photons travel at the same speed as they had shortly after the inception of the cosmos. This is the true upper limit velocity in the vacuum. Since the movement of light photons between VPP interactions is an electromagnetic phenomenon, then the movement of the electrically charged VPP’s in the vacuum is also an electromagnetic phenomenon. It is important to note that there is nothing to inhibit the motion of the VPP’s themselves. They must always move at the upper limit velocity for the cosmos which seems to be 1.1 x 10^10 times the speed of light now.
With that fact in mind, we note that all sub-atomic particles like electrons, protons or neutrons (which may be considered to be an electron and proton together – or made up of quarks), all carry an intrinsic charge. The mere presence of the charge on these particles polarizes the vacuum around them. Thus, an electron becomes surrounded by a layer of positively charged virtual particles which in turn is surrounded by a layer of negatively charged virtual particles, and so on out into the vacuum. This vacuum polarization acts to attract other virtual particles which may be nearby. The sign of the charge initially attracted does not matter; it only affects the phase of the interactions. If the virtual particle-pair is considered to be a single entity, then that pair has a positive end and a negative end. Thus one end of the single particle-pair entity will be attracted to the charge of opposite sign. So, however this is envisaged, there is a resulting re-orientation of virtual particle pairs in the vacuum; the vacuum is polarized.
This vacuum polarization acts to attract sub-atomic particles, protons, electrons, or quarks which may be nearby. This net attractive force between sub-atomic particles caused by vacuum polarization has been shown by SED physicists to be quantitatively identical to gravity. So, the larger the collection of particles, the stronger is the resulting attraction we call gravity. Haisch concluded his explanation when he said, “This might explain why gravity is so weak. One mass does not pull directly on another mass but only through the intermediary of the [charged virtual particles that make up the] vacuum.” [95] On this basis, then, gravitation and mass may be considered to be simply manifestations of electromagnetic effects linked with the ZPE."
The speed at which these gravitational interactions occur is then dependent entirely on the speed at which the virtual particles come together in the vacuum polarization process, which is the origin of gravity. This can be deduced from standard equations relating to the kinetic energy ( ½ m v^2) of one
charged particle in the field of another (q^2/[2rε]) where “q” is the charge, “r” is the distance apart, and “ε” is the electric permittivity of the vacuum and m is the mass of the particle and v its velocity. This is the velocity with which the particles come together after traveling a distance “r.” Thus the equation starts as …
½ mv^2 = q^2 / [2rε]
So we obtain from this
v^2 = q^2 / [mrε] = (q^2 / ε ) (1 / [mr])
Earlier work in the Monograph has shown that with a varying ZPE the quantity (q^2 / ε) remains unchanged. This quantity shows that velocity of approach of the virtual particles does not change with any ZPE changes. However, we need to consider the quantity (mr) with ZPR variation. As the cosmos expanded, the ZPE built up. Consequently, more virtual particle pairs per unit volume came into existence. The analysis in the Monograph shows that the mass of those particles, m, is proportional to the square of ZPE strength. In addition, the distance apart of the charges, r, will lessen as the ZPE builds up. Analysis suggests that r is inversely proportional to ZPE strength. Thus the quantity (mr) will remain constant.
The ultimate outcome is that the velocity of transmittal of the effects causing gravity are, first, unchanged as the ZPE varies with time, and, second, that velocity or speed is of the order of 10^10 times the current speed of light, just as Van Flandern’s analysis indicated.
![]()
Lambert's Main Library
Email is welcome: Lambert Dolphin
Archive for Newsletters
Library Annex (new articles since 2018)
April 27, 1999, February 6, 2000, September 24, 2021. December 22, 2022.
